Chemistry notes
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Are you struggling to draw the Lewis dot structure of different elements and molecules? Do you find yourself lost in a web of lines and dots, not knowing where to start or how to proceed? Fear not, for drawing Lewis dot structures is easier than you think! In this article, we will guide you through the process of drawing Lewis dot structures step-by-step, and by the end of this article, you will be able to draw the structures with ease.
The process of drawing Lewis dot structures can be intimidating, especially for beginners who are new to the concept. Many students struggle with understanding the basic rules and principles of Lewis dot structures, which can hinder their progress in chemistry. However, with a little guidance and practice, anyone can master the technique of drawing Lewis dot structures.
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of Lewis dot structures, let’s first understand what they are and why we need to draw them. The Lewis dot structure is a symbolic representation of the valence electrons of an atom or molecule, where dots are used to represent electrons and lines used to represent covalent bonds. The Lewis dot structure helps us to understand how atoms combine to form molecules, which is essential in predicting the reactivity and behavior of molecules.
To draw a Lewis dot structure, you need to follow a series of steps. Firstly, you need to determine the total number of valence electrons for the atoms in the molecule. Secondly, you need to determine the central atom, which is usually the least electronegative atom in the molecule. Thirdly, you need to determine the number of bonds each atom can form based on their valency. Finally, you need to distribute the remaining electrons as lone pairs on the atoms.
In summary, drawing Lewis dot structures involves determining the total number of valence electrons, identifying the central atom, determining the number of bonds each atom can form, and distributing the remaining electrons as lone pairs on the atoms.
My Personal Experience with Drawing Lewis Dot Structures
When I first started learning chemistry, I was intimidated by the concept of Lewis dot structures. It seemed like a web of lines and dots that made no sense to me. However, with the help of my chemistry teacher, I gradually learned the technique of drawing Lewis dot structures. I practiced drawing different structures repeatedly till I could draw them with ease. Drawing Lewis dot structures is now one of my favorite things to do in chemistry.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Draw Lewis Dot Structures
To draw a Lewis dot structure, follow these step-by-step instructions:
Step 1: Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons
The first step in drawing a Lewis dot structure is to determine the total number of valence electrons for the atoms in the molecule. To do this, you need to know the electronic configuration of the atoms. The valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of the atom, and they determine the reactivity of the atom.
For example, let’s take the molecule H2O. Oxygen has 6 valence electrons, and hydrogen has 1 valence electron each. Therefore, the total number of valence electrons for H2O is:
Total no. of valence electrons = no. of valence electrons for oxygen + no. of valence electrons for hydrogen
Total no. of valence electrons in H2O = 6 + (1 x 2) = 8
Therefore, H2O has a total of 8 valence electrons.
Step 2: Identify the Central Atom
The second step in drawing a Lewis dot structure is to identify the central atom. The central atom is usually the least electronegative atom in the molecule, except in the case of hydrogen. The electronegativity of an atom determines the number of electrons it can attract towards itself.
In the case of H2O, oxygen is the central atom because it is the most electronegative atom in the molecule. The hydrogen atoms are peripheral atoms.
Step 3: Determine the Number of Bonds Each Atom Can Form
The third step in drawing a Lewis dot structure is to determine the number of bonds each atom can form based on their valency. The valency of an atom refers to the number of bonds it can form with other atoms.
In the case of H2O, oxygen can form two bonds, and each hydrogen atom can form one bond. Therefore, H2O has two single bonds between oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
Step 4: Distribute the Remaining Electrons as Lone Pairs on the Atoms
The final step in drawing a Lewis dot structure is to distribute the remaining electrons as lone pairs on the atoms. Lone pairs are pairs of valence electrons that are not involved in bond formation.
In the case of H2O, we have already used four electrons in the bonds between hydrogen and oxygen. Therefore, we have four remaining electrons that need to be distributed as lone pairs. Since oxygen has two lone pairs, each hydrogen atom has no lone pairs.
The final structure of H2O can be represented as:
 ### Advanced Tips for Drawing Lewis Dot Structures
### Advanced Tips for Drawing Lewis Dot Structures
Here are some advanced tips to keep in mind when drawing Lewis dot structures:
Tip 1: Formal Charge
Formal charge is the charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, assuming that electrons are shared equally between atoms in a covalent bond. The formal charge of an atom can be calculated by the following formula:
Formal charge = no. of valence electrons - (no. of lone pair electrons + 0.5 x no. of bonding electrons)
If the formal charge of an atom is zero, the Lewis dot structure is usually more stable.
Tip 2: Resonance Structures
Resonance structures are the different possible arrangements of electrons in a molecule where the positions of atoms remain the same. Resonance structures are used to represent the delocalization of electrons in a molecule, which is common in molecules like benzene.
Tip 3: Exceptions to Octet Rule
There are some exceptions to the octet rule, where certain atoms can exceed the eight valence electrons. This is common for elements in the third row and below in the periodic table, like sulfur and phosphorus. These elements can form compounds where they have more than eight valence electrons.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Why do we need to draw Lewis dot structures?
A: Lewis dot structures help us to understand how atoms combine to form molecules, which is essential in predicting the reactivity and behavior of molecules.
Q2: What is the valency of an atom?
A: The valency of an atom refers to the number of bonds it can form with other atoms.
Q3: How do I determine the central atom in a molecule?
A: The central atom is usually the least electronegative atom in the molecule, except in the case of hydrogen.
Q4: What are lone pairs?
A: Lone pairs are pairs of valence electrons that are not involved in bond formation.
Conclusion of How to Draw Lewis Dot Structures
Drawing Lewis dot structures is a fundamental concept in chemistry that is essential for understanding how atoms combine to form molecules. By following the steps outlined in this article, you should be able to draw Lewis dot structures with ease. Remember to practice drawing different structures repeatedly to gain confidence in the technique.
Gallery
Chemistry Notes

Photo Credit by: bing.com /
Lewis Diagrams Made Easy: How To Draw Lewis Dot Structures - YouTube
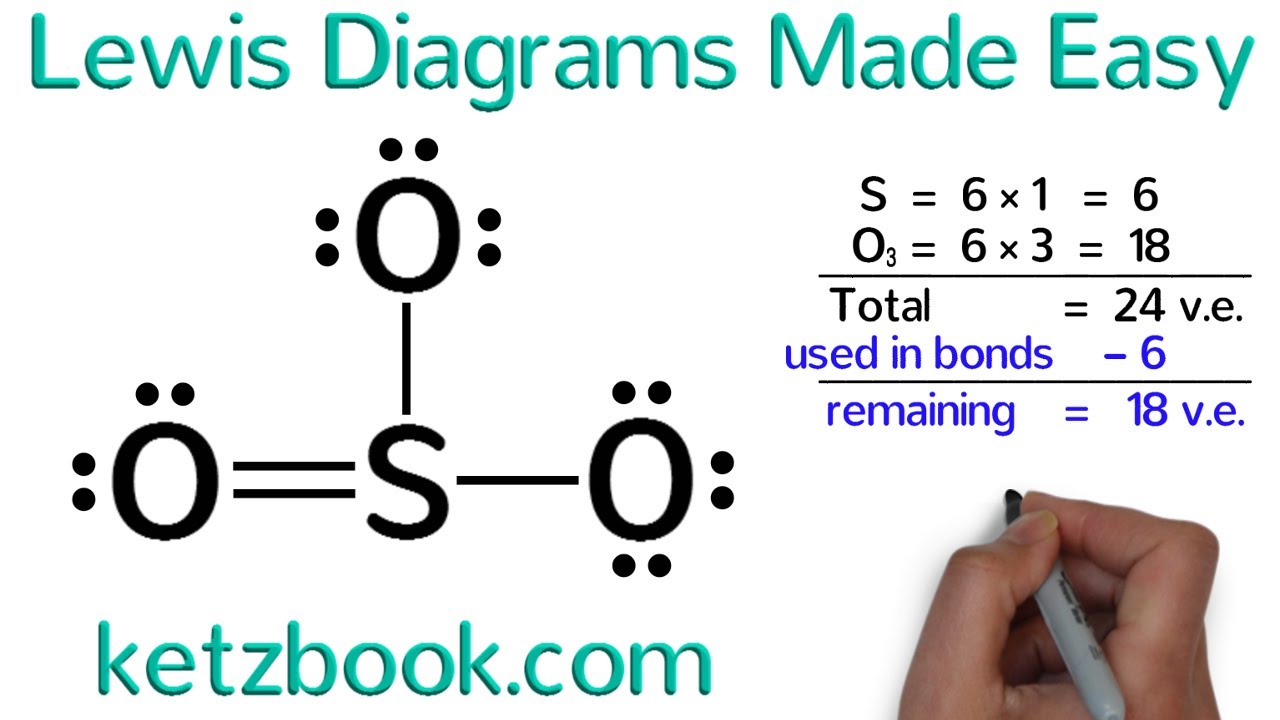
Photo Credit by: bing.com / lewis dot draw structures diagrams easy made
Lewis Structure | Chemistry Classroom, Teaching Chemistry, Chemistry

Photo Credit by: bing.com / lewis structure dot draw chemistry molecular structures infographic notes worksheet organic classroom help simple geometry drawing diagram electron worksheets babe
How To Draw Lewis Dot Structure
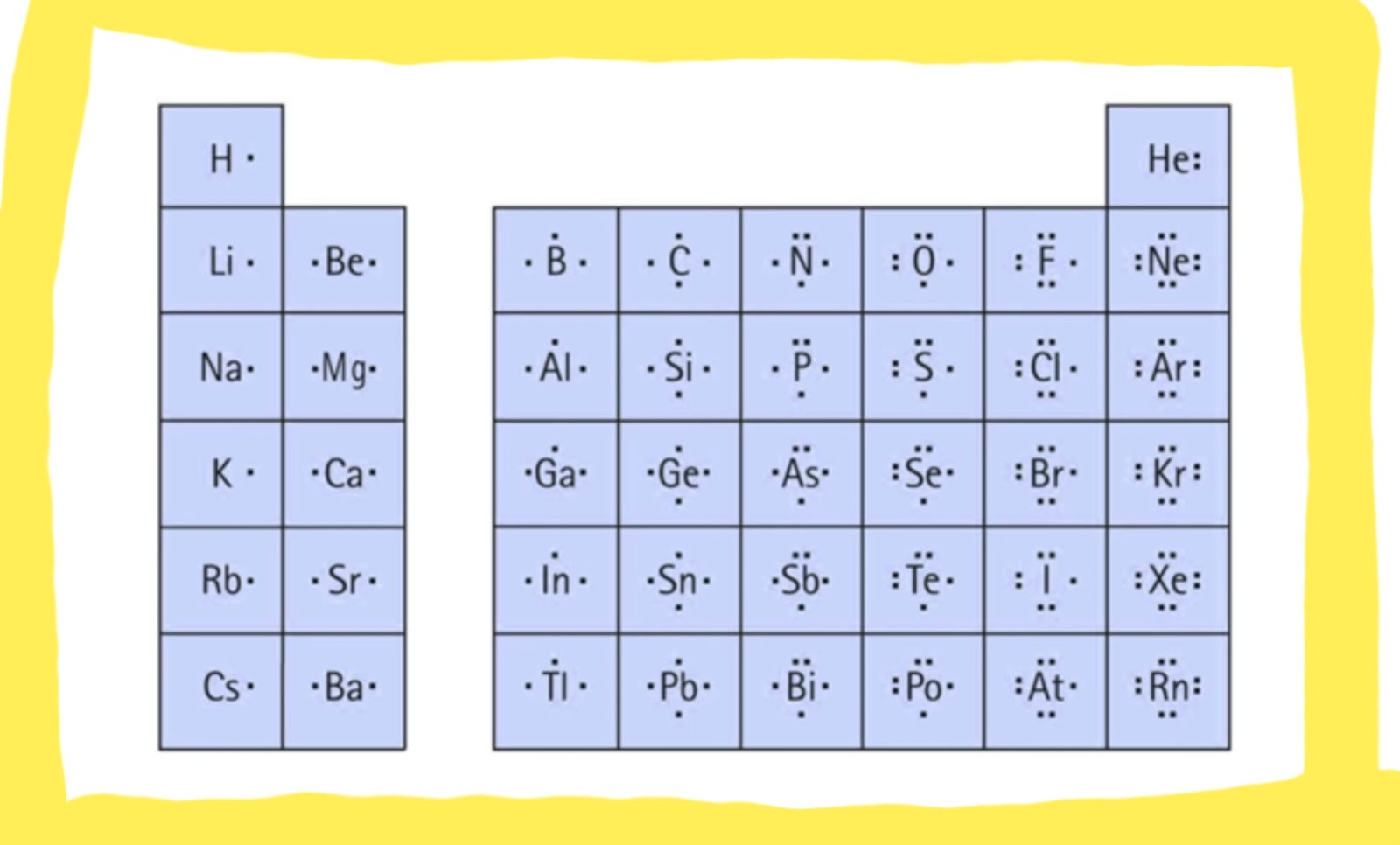
Photo Credit by: bing.com / lewis dot structure structures diagram valence draw electrons drawing represent often used number
How To Draw A Lewis Structure

Photo Credit by: bing.com / lewis structure dot draw formaldehyde